In the world of manufacturing, plastic moulds are the silent workhorses behind the creation of thousands of everyday products. From automotive parts and electronic housings to medical devices and kitchenware, plastic moulds enable the mass production of precise, durable, and cost-effective components.
But what exactly are these moulds? What types are available? And how do they influence the final product quality?
Let’s dive deep into the world of plastic moulds, their types, applications, and why choosing the right mould is critical for your product’s success.
What is a Plastic Mould?
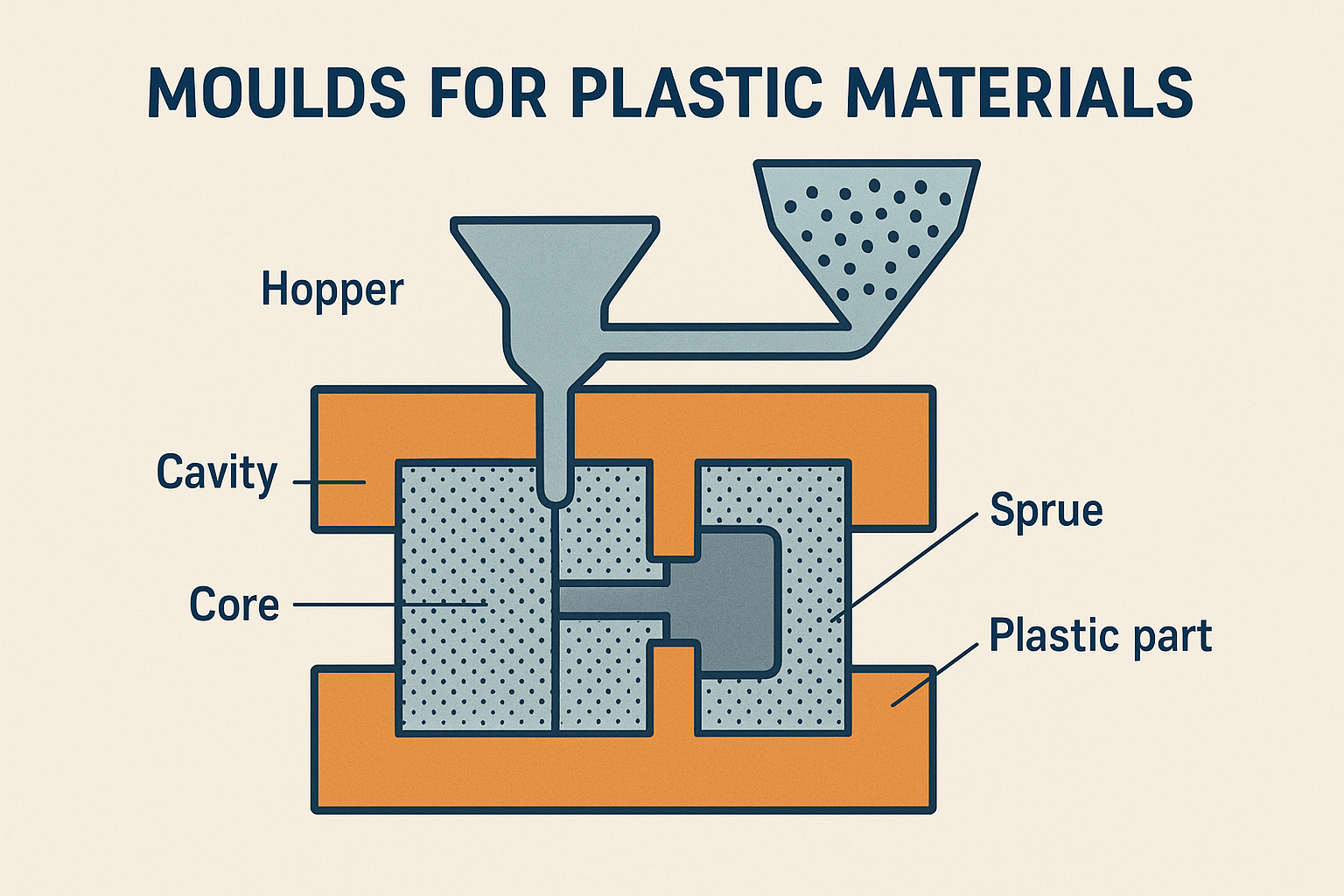
A Plastic mould is a hollow metal block into which molten plastic material is injected to form a specific shape once it cools and solidifies. These moulds are typically made from hardened steel, pre-hardened steel, aluminum, or beryllium-copper alloys depending on the application and production volume.
The mould design defines everything about the plastic part — its size, shape, thickness, tolerance, texture, and finish.
The process used is known as plastic injection molding, one of the most common manufacturing methods for thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
Types of Moulds Used in Plastic Molding
There are several types of plastic moulds, each suited for different production needs and part designs. Here are the most commonly used types:
- Injection Moulds
Injection moulds are the most widely used moulds in the plastics industry. These are high-precision moulds used to produce complex plastic components with tight tolerances. Molten plastic is injected at high pressure into the mould cavity, cooled, and ejected once solid.
Applications: Automotive parts, appliance housings, toys, electronic enclosures.
Advantages:
- High volume production
- Consistent quality
- Supports complex geometries
- Blow Moulds
Blow moulding is used to create hollow plastic products. The process involves inflating heated plastic into a mould cavity using air pressure.
Applications: Bottles, containers, fuel tanks, plastic drums.
Advantages:
- Ideal for hollow products
- Low material waste
- Quick cycle times
- Compression Moulds
Compression moulding involves placing preheated plastic material into a heated mould cavity, closing the mould, and applying pressure until the material fills the cavity and cures.
Applications: Electrical components, rubber parts, automotive panels.
Advantages:
- Good for high-strength parts
- Suitable for thermosetting plastics
- Low tooling cost
- Extrusion Moulds (Dies)
These moulds are used in the extrusion process, where melted plastic is pushed through a die to create continuous shapes like pipes, rods, or profiles.
Applications: Pipes, tubes, window frames, cable insulation.
Advantages:
- Continuous production
- Simple mould (die) design
- Minimal scrap
- Rotational Moulds
In rotational moulding, powdered plastic is placed in a mould which is then heated and rotated so that the plastic melts and coats the interior of the mould.
Applications: Water tanks, large containers, playground equipment.
Advantages:
- No seams or welds
- Low tooling cost
- Excellent for large parts
- Thermoforming Moulds
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet until pliable, then forming it over a mould using vacuum or pressure.
Applications: Packaging trays, clamshells, disposable cups, automotive panels.
Advantages:
- Low tooling cost
- Fast prototyping
- Great for thin-wall applications
Key Considerations When Choosing a Plastic Mould
Choosing the right mould type depends on several factors:
- Production volume: Injection moulds are ideal for high-volume runs; thermoforming suits lower volumes.
- Material compatibility: Not all plastics behave the same. Moulds must be designed to handle specific polymers.
- Part complexity: Complex parts require multi-cavity or custom-designed moulds.
- Surface finish: Some moulds can produce high-gloss finishes, while others are suited for textured or matte surfaces.
- Budget: Moulds vary greatly in cost; for example, injection moulds are more expensive upfront but cost-effective long term.
Why Mould Quality Matters
The quality of the mould directly affects the quality, strength, and appearance of the final product. Poorly made moulds can lead to defects such as warping, sink marks, flash, and inconsistent dimensions — which can damage your brand and increase manufacturing costs.
That’s why it’s crucial to partner with an experienced and trusted mould manufacturer who understands not just the tooling, but the entire production lifecycle.
Partner with Northern Plastics Engg – Your Trusted Mould Manufacturing Experts
At Northern Plastics Engg, we specialize in the design and manufacturing of precision plastic moulds for a wide range of applications. With years of experience in injection moulding, mould base manufacturing, and die tooling, we deliver high-performance solutions tailored to your production needs.
Whether you’re developing a new product or upgrading an existing one, our team is committed to providing:
✅ High-precision custom moulds
✅ In-house design and tooling support
✅ Durable, high-quality steel and aluminum moulds
✅ Quick turnaround and post-sales support
✅ Competitive pricing and scalability